

Office of solid waste management and emergency response (5306P), EPA530-R-08-010, November. USEPA (2008) Municipal solid waste in the United States: 2007 facts and figures. Office of solid waste management and emergency response (5305W), EPA530-S-02-001, June. USEPA (2002) Municipal solid waste in the United States: 2000 facts and figures. KeywordsĪl-Salem SM, Lettieri P, Baeyens J (2009) Recycling and recovery routes of plastic solid waste (PSW): a review. The rapid biodegradation of PS and PE is likely a result of synergistic effects of intestinal microbial activities and host digestive system, and further research is needed to understand the mechanisms. molitor, but they grow on plastics slowly. A few plastic-degrading gut bacterial strains have been isolated from gut of T. Gut microbial communities shifted after the larvae were fed with PS or PE. Co-feeding normal diet (e.g., bran) enhances PS and PE consumption rate significantly.

Ingested PS or PE supports the larvae with energy for life activities but not growth. Ingested PS or LDPE polymer can be depolymerized by up 60–70% within 12–24 h after 1- or 2-week adaption. The biodegradation was evaluated on the basis of plastic mass balance, modification of ingested polymers, formation of biodegraded intermediates, as well as 13C isotopic tracer tests.

molitor larvae also degrade low-density polyethylene (LDPE).
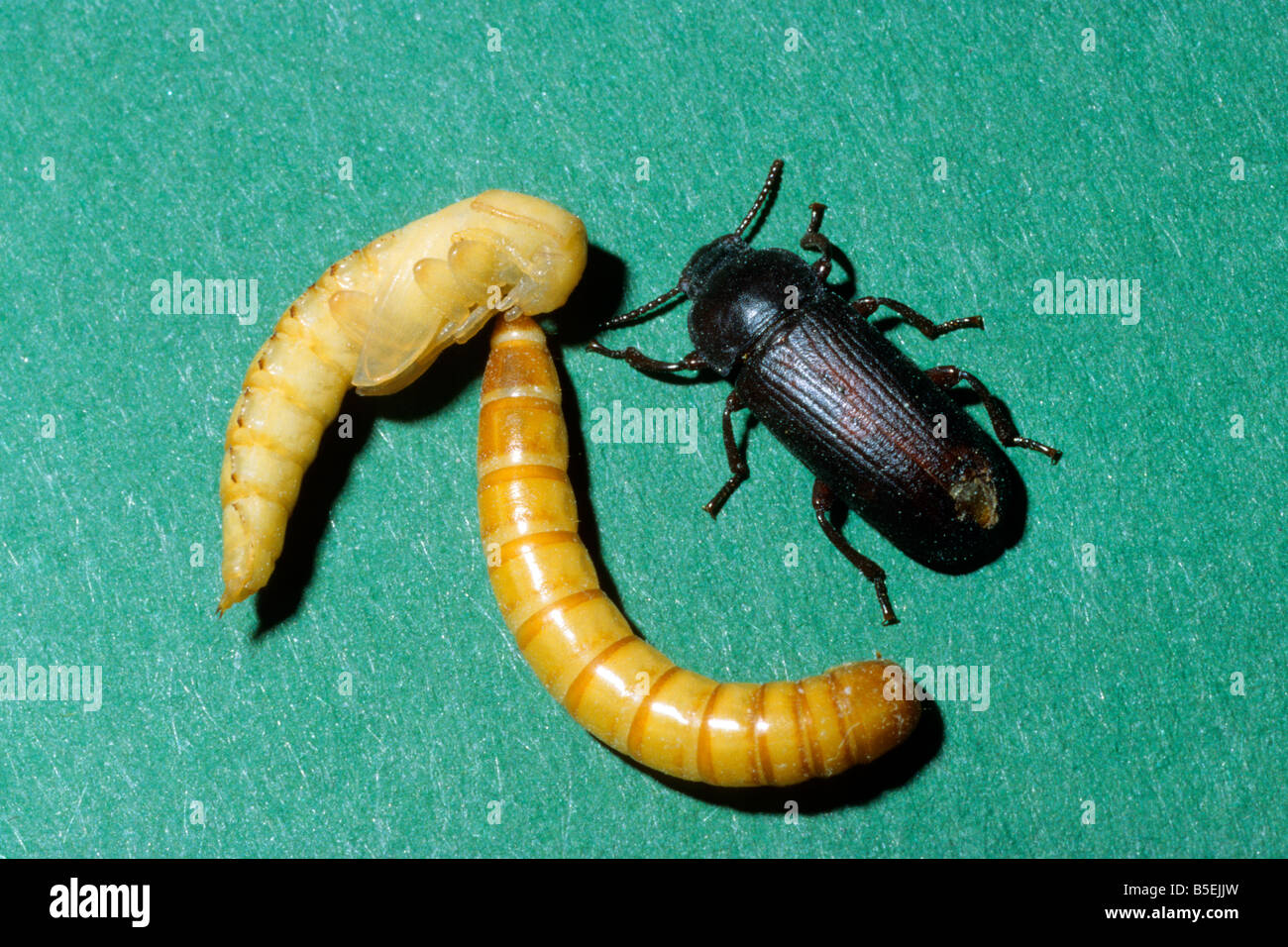
The larvae of darkling beetles (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae), especially Tenebrio molitor and Tenebrio obscurus larvae, showed the capacity of rapid gut microbe-dependent degradation of polystyrene (PS). Observation of damage, penetration, and ingestion of plastics by insects and their larvae lead to research on biodegradation of plastics by insects. Most petroleum-based plastics are resistant to biodegradation in the environment.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
